Nagoya University researchers have trained an AI to predict the orientation of crystal grains in polycrystalline materials using optical images, significantly reducing analysis time from 14 hours to 1.5 hours. This advancement, detailed in APL Machine Learning, promises to revolutionize the use of these materials in industries like electronics and solar energy.
Japanese researchers have developed an AI that quickly predicts crystal orientations in industrial materials, paving the way for more efficient use of polycrystalline components in technology.
A team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan has made a significant breakthrough in predicting crystal orientation. They accomplished this by training an artificial intelligence (AI) model using optical photographs of polycrystalline materials. This innovative research was published in the journal APL Machine Learning.
The Importance of Crystals in Industry
Crystals are a vital component of many machines. Familiar materials used in industry contain polycrystalline components, including metal alloys, ceramics, and semiconductors. As polycrystals are made up of many crystals, they have a complex microstructure, and their properties vary greatly depending on how the crystal grains are orientated. This is especially important for the silicon crystals used in solar cells, smartphones, and computers.
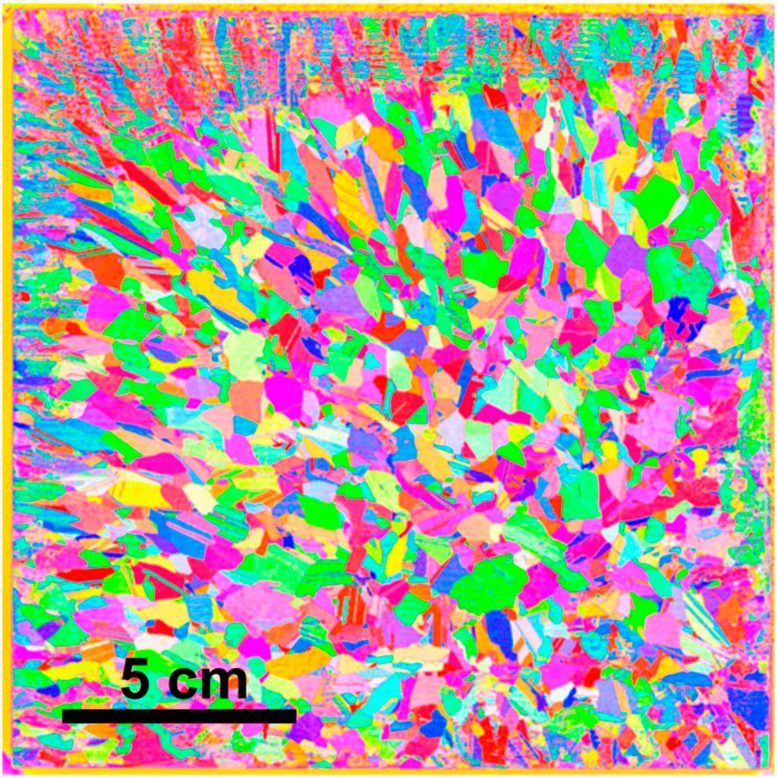
An example of the crystal grain orientations predicted by the AI-based technique. The color represents the orientation of the grain. Credit: Dr. Takuto Kojima
Challenges in Polycrystalline Material Analysis
“To obtain a polycrystalline material that can be used effectively in industry, control and measurement of grain orientation distribution is required,” Professor Noritaka Usami said. “However, this is hindered by the expensive equipment and time current techniques needed to measure large-area samples.”
Innovative AI Application in Crystal Orientation Prediction
A Nagoya University team consisting of Professor Usami from the Graduate School of Engineering and Professor Hiroaki Kudo from the Graduate School of Informatics, in collaboration with RIKEN, have applied a machine learning model that assesses photographs taken by illuminating the surface of a polycrystalline silicon material from various directions. They found that the AI successfully predicted the grain orientation distribution.
Researchers took many photographs by illuminating the surface of a multicrystalline silicon material from various directions. These photos were used to train the machine learning model. Credit: Dr. Takuto Kojima
Efficiency and Potential Industrial Applications
“The time required for this measurement was about 1.5 hours for taking optical photographs, training the machine learning model, and predicting the orientation, which is much faster than conventional techniques, which take about 14 hours,” Usami said. “It also enables measurement of large-area materials that were impossible with conventional methods.”
Usami has high hopes for the use of the team’s technique in industry. “This is a technology that will revolutionize materials development,” Usami said. “This research is intended for all researchers and engineers who develop polycrystalline materials. It would be possible to manufacture an orientation analysis system of polycrystalline materials that packages an image data collection and a crystal orientation prediction model based on machine learning. We expect that many companies dealing with polycrystalline materials would install such equipment.”
Reference: “A machine learning-based prediction of crystal orientations for multicrystalline materials” by Kyoka Hara, Takuto Kojima, Kentaro Kutsukake, Hiroaki Kudo and Noritaka Usami, 24 May 2023, APL Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0138099


