It’s no fun as a customer to have an interaction with a bot when it’s clearly a bot with which you’re engaging.
Rasa is a startup that claims to have developed the infrastructure to give developers at large enterprises the ability to build “robust” generative conversational AI assistants so that those interactions feel more personal and meaningful to users. It says it does this by providing the infrastructure CALM (Conversational AI with Language Models) and a low-code user interface.
Its technology has helped it land a number of large clients, mainly in the financial services and telecom space. Those customers include two of the world’s three top banks, two of the largest banks in the United States, American Express and Deutsche Telekom, among others.
Founded in 2016, Rasa started out as an open source platform for developers to build chatbots, voice apps and other services that employ conversational AI for interactivity. Since then, Rasa has been downloaded by developers more than 50 million times, the company claims.
A few years ago, the startup recognized the opportunity to help enterprises drive better engagement with their customers. Oracle alum CEO Melissa Gordon was brought in to help lead that new strategy. Gordon, who was a pole vaulter for many years in a sport when it wasn’t a female sport and used Title IX to compete on the men’s team, said she likes “to challenge the status quo.”
“We’ve always been very vocal from the start about challenging some of the established ideas about how chatbots are going to be built,” said co-founder and CTO Alan Nichol.
The move seems to have paid off for Rasa, who says it “roughly doubled” its annual recurring revenue (ARR) in 2023 compared to the year prior. That traction helped it land $30 million in Series C funding co-led by StepStone Group and PayPal Ventures, participation from existing backers Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Accel and Basis Set Ventures. The company declined to reveal valuation, saying only it was an up round from its $26 million Series B raise.
There’s no doubt the space is a hot — and increasingly crowded — one. On Tuesday, TechCrunch reported on Sierra, a conversational AI startup founded by former Salesforce co-CEO Bret Taylor and former Google employee Clay Bavor that claims its software can actually take actions on behalf of the customer.
Rasa is different, Nichol said, in that it’s not all about agents.
What the two companies do have in common is they both claim to be addressing issues like hallucinations, where a large language model sometimes makes up an answer when it lacks the information to answer accurately.
Rasa claims that it’s unique in that it lets businesses “leverage the full power of LLMs to understand language in a really nuanced way, without opening yourself up to these kinds of risks.” In other words, it says it uses LLMs to understand users, rather than to guess business logic or lead a conversation so that enterprises can retain control over the way conversations go and the things their bots say.
It’s a bold claim.
But as a result, Gordon says, the bots that Rasa’s infrastructure helps develop don’t feel like branded bots.
“A classic use case is a customer-facing flagship assistant, and typically, these teams when they come to Rasa, it’s usually not their first rodeo,” Nichol said. “They’ve been on another platform or they’ve tried to build everything in house. And then at some point, they’ve run out of steam, and then they’re looking for something that’s more scalable.”
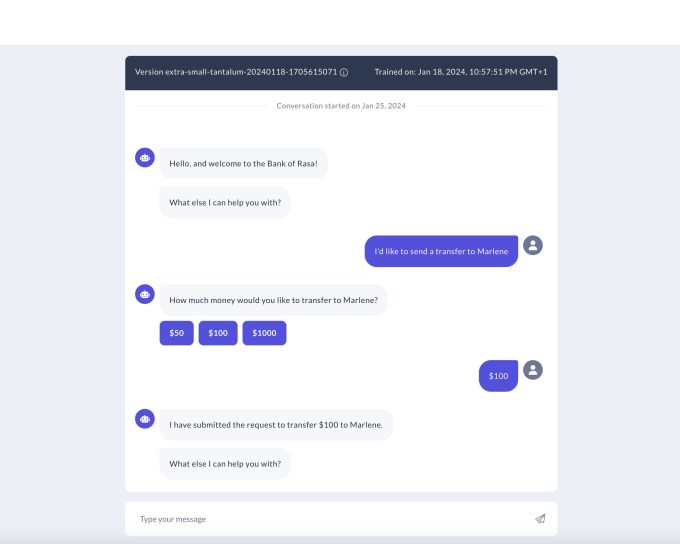
Image Credits: Rasa
The bots have external use cases ranging from checking account balances to transferring money. In the case of Deutsche Telekom, for example, bots can help with resetting a router in someone’s house if they have an internet problem, Gordon points out. Notably, the investment marks PayPal Ventures’ first investment in AI. In a written statement, partner Alan Du said: “At PayPal we have seen how Rasa’s technology improves customer engagement and business performance through our concierge solutions, and we are making our first AI investment in Rasa because we believe it is the best platform for enterprises to develop robust conversational AI.”


