
Microsoft Bing is getting a new “Deep Search” feature powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4. The feature is designed to give users more relevant and comprehensive answers to complex search queries. Microsoft notes that Deep Search is not a replacement for Bing’s existing web search, and is instead an enhancement that allows for deeper exploration of the web.
In a blog post, Microsoft explains that the new feature builds on Bing’s current web index and ranking system and enhances them with GPT-4, which takes the search query and turns it into a more comprehensive description of what the results should include.
For instance, say a user is looking into loyalty programs in different countries and enters the query: “how do points systems work in Japan.” Deep Search would take the query and expand it into the following:
Provide an explanation of how various loyalty card programs work in Japan, including the benefits, requirements, and limitations of each. Include examples of popular loyalty cards from different categories, such as convenience stores, supermarkets, and restaurants. Show a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of using loyalty cards versus other payment methods in Japan, including current rewards and benefits. Highlight the most popular services and participating merchants.
With this expanded description, you are able to explain your intent better than you could with just a few words.
In instances where your search query is more ambiguous, Deep Search will find all of the possible intents and creates a comprehensive description for each of them. Deep Search then displays these intents to you, allowing you to select the right one.
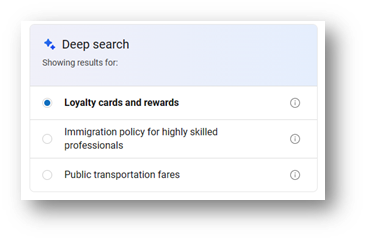
Image Credits: Bing
Once the expanded description has been created, Bing will pull relevant results that often don’t show up in typical search results, Microsoft says. Deep Search finds pages that might match the expanded query, rewrites the query and then searches for those variations too.
Sticking with the same loyalty points query example above, Deep Search may also search for things like “loyalty card programs Japan,” “best loyalty cards for travelers in Japan,” “comparison of loyalty programs by category in Japan,” “redeeming loyalty cards in Japan” and “managing loyalty points withe phone apps.”
“By doing this, Deep Search can find results that cover different aspects of my query, even if they don’t explicitly include the original keywords,” Microsoft wrote in the blog post. “Regular searches on Bing already consider millions of web pages for each search and Deep Search does ten times that to find results that are more informative and specific than the ones that rank higher in normal search.”
Once Deep Search has collected web pages, it ranks them based on how well they match the expanded description. When ranking, Deep Search considers how well the topic matches the query, whether it has an appropriate level of details, how trustworthy the page is and how new and popular it is.
Microsoft notes that Deep Search is optional and can take up to 30 seconds to complete, which is why it’s not meant for every query or user. For users who don’t want more comprehensive answers, they can get regular Bing search results instantly.


