New art work created by synthetic intelligence does bizarre issues to the primate mind.
When proven to macaques, AI-generated photos purposefully precipitated nerve cells within the monkeys’ brains to fireplace greater than footage of real-world objects. The AI may additionally design patterns that activated particular neurons whereas suppressing others, researchers report within the Might 3 Science.
This unprecedented control over neural activity using images could result in new sorts of neuroscience experiments or therapies for psychological issues. The AI’s capability to play the primate mind like a fiddle additionally gives perception into how intently AIs can emulate mind perform.
The AI liable for the brand new mind-bending photos is a synthetic neural community — a pc mannequin composed of digital neurons — modeled after the ventral stream. It is a neural pathway within the mind concerned in imaginative and prescient (SN On-line: 8/12/09). The AI discovered to “see” by learning a library of about 1.3 million labeled photos. Researchers then instructed the AI to design footage that will have an effect on particular ventral stream neurons within the mind.
Viewing any picture triggers some type of neural exercise in a mind. However neuroscientist Kohitij Kar of MIT and colleagues wished to see whether or not the AI’s intentionally designed photos may induce particular neural responses of the workforce’s selecting. The researchers confirmed these photos to a few macaques fitted with neuron-monitoring microelectrodes.
In a single experiment, the AI aimed to create patterns that will activate neurons at a selected website within the ventral stream as a lot as doable, no matter the way it affected different neurons. In 40 of the 59 neural websites examined, AI-made footage precipitated neurons to fireplace greater than any picture of a real-world object, resembling a bear, a automobile or a face. The AI’s photos usually precipitated neurons to fireplace 39 p.c greater than their most response to real-world photos. Even when the monkeys have been proven patterns beforehand designed by researchers particularly to set off ventral stream neurons, the AI designs made these neurons hearth at greater charges.
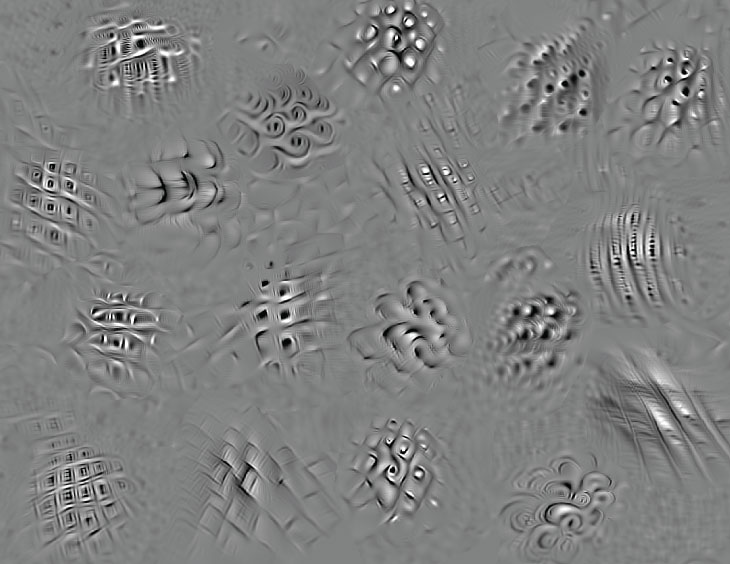
In one other take a look at, the AI crafted patterns meant to make the neurons at one goal website go wild, whereas minimizing the exercise of others. For 25 of 33 websites, AI-created photos remoted neural exercise to the goal website considerably higher than real-world photos. Though this manipulation shouldn’t be but good, future AIs with extra refined designs and extra coaching knowledge could wield finer management, says research coauthor Pouya Bashivan, a computational neuroscientist at MIT.
“That is magnificent technical progress,” says Arash Afraz, a neuroscientist on the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being in Bethesda, Md., not concerned within the research.
In neuroscience experiments, researchers “could wish to induce a selected sample of exercise within the mind” to be taught what totally different neurons are liable for, Afraz says. “The direct approach of doing that’s to roll your sleeves up, open up the cranium and stick one thing in there,” like electrodes. “Now, we now have a brand new software in our toolbox” to noninvasively tinker with neurons in ways in which weren’t doable earlier than.
AI-rendered photos that orchestrate neural exercise can also result in new therapies for psychological well being issues like post-traumatic stress dysfunction, anxiousness or “something that must do with temper,” Bashivan says. Just like the way in which that individuals use light therapy boxes to assuage seasonal affective disorder (SN: 4/23/05, p. 261) or take a look at peaceful nature scenes to calm down (SN: 11/10/18, p. 16), folks could sometime be soothed by gazing upon photos that an AI tailored to spice up temper.
These experiments not solely show a brand new approach to control neurons, but additionally present new perception into the character of AI. Synthetic neural networks are neuroscientists’ finest laptop fashions of the ventral stream. The digital neurons in these laptop applications are organized the same structure as organic ones, and these AIs are nice at recognizing objects in pictures. However there’s been some debate about how really brainlike these AIs are, by way of how they course of and perceive visible inputs, says Ed Connor, a neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins College not concerned within the work.
The truth that monkey neurons responded to AI-created photos simply because the AI meant means that this laptop program does certainly perceive visible data in a approach that’s just like the primate mind, Connor says. “This nails it in a approach that may persuade skeptics, together with myself.”
If synthetic neural networks truly “see” in a approach that intently mimics the mind, learning these AI applications could assist scientists higher perceive human imaginative and prescient. Researchers of the long run may forgo monkeys and mice, and probe neural goings-on inside AIs instead (SN: 6/9/18, p. 14).
Experimenting on such digital neurons may supply “a approach of letting you do any dream experiment you prefer to on a system that’s fully accessible in a approach that the mind isn’t,” Connor says.


