Synthetic intelligence can share our pure potential to make numeric snap judgments.
Researchers noticed this knack for numbers in a pc mannequin composed of digital mind cells, or neurons, known as a man-made neural community. After being skilled merely to determine objects in photos — a standard activity for AI — the community developed digital neurons that reply to particular portions. These synthetic neurons are harking back to the “quantity neurons” thought to provide humans, birds, bees and different creatures the innate potential to estimate the variety of gadgets in a set (SN: 7/7/18, p. 7). This instinct is named quantity sense.
In number-judging duties, the AI demonstrated a quantity sense much like people and animals, researchers report on-line Might 8 in Science Advances. This discovering lends perception into what AI can study with out specific instruction, and will show attention-grabbing for scientists learning how quantity sensitivity arises in animals.
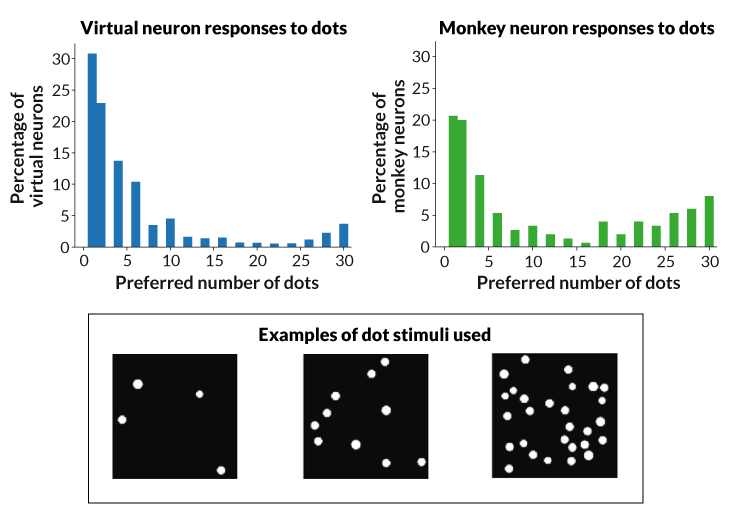
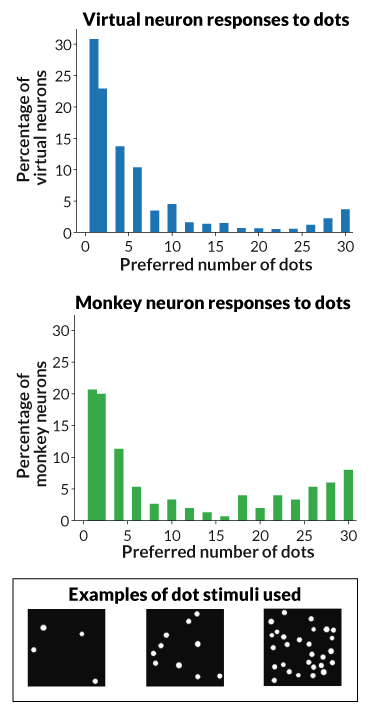
Neurobiologist Andreas Nieder of the College of Tübingen in Germany and colleagues used a library of about 1.2 million labeled photos to show a man-made neural community to acknowledge objects equivalent to animals and autos in footage. The researchers then introduced the AI with dot patterns containing one to 30 dots and recorded how varied digital neurons responded.
Some neurons had been extra energetic when viewing patterns with particular numbers of dots. As an example, some neurons activated strongly when proven two dots however not 20, and vice versa. The diploma to which these neurons most well-liked sure numbers was almost similar to earlier information from the neurons of monkeys.
To check whether or not the AI’s quantity neurons geared up it with an animal-like quantity sense, Nieder’s workforce introduced pairs of dot patterns and requested whether or not the patterns contained the identical variety of dots. The AI was appropriate 81 % of the time, performing about in addition to people and monkeys do on related matching duties. Like humans and other animals, the AI struggled to distinguish between patterns that had very related numbers of dots, and between patterns that had many dots (SN: 12/10/16, p. 22).
This discovering is a “very good demonstration” of how AI can decide up a number of abilities whereas coaching for a selected activity, says Elias Issa, a neuroscientist at Columbia College not concerned within the work. However precisely how and why quantity sense arose inside this synthetic neural community continues to be unclear, he says.
Nieder and colleagues argue that the emergence of quantity sense in AI would possibly assist biologists perceive how human infants and wild animals get a quantity sense with out being taught to rely. Maybe primary quantity sensitivity “is wired into the structure of our visible system,” Nieder says.
Ivilin Stoianov, a computational neuroscientist on the Italian Nationwide Analysis Council in Padova, shouldn’t be satisfied that such a direct parallel exists between the quantity sense on this AI and that in animal brains. This AI realized to “see” by learning many labeled footage, which isn’t how infants and wild animals study to make sense of the world. Future experiments might discover whether or not related quantity neurons emerge in AI techniques that extra carefully mimic how organic brains study, like those that use reinforcement learning, Stoianov says (SN: 12/8/18, p. 14).
.image-mobile {
show: none;
}
@media (max-width: 400px) {
.image-mobile {
show: block;
}
.image-desktop {
show: none;
}
}